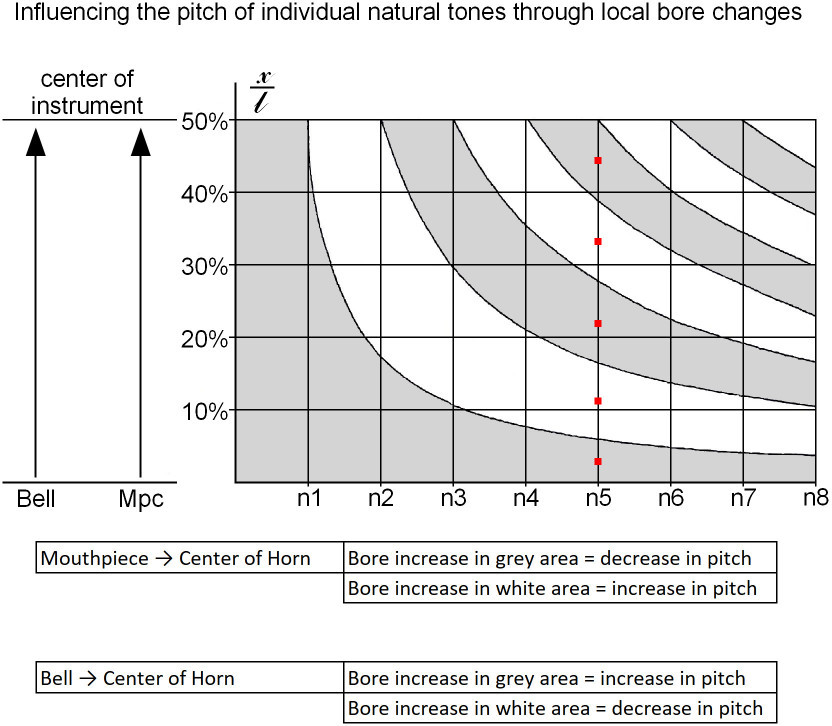
For example, look at the red dots above. These dots represent the nodes and antinodes for the 5th natural note (on the trumpet, that would be e2); simply mark the position exactly in the center of the grey or white regions along the n5 line. The distance can by found on the left side of the chart.
• "Length" = Instrument length from the mouthpiece rim to the end of the bell, with instrument tuned.
• When possible, adjust the middle of the instrument to minimise affecting multiple notes. Leave the bell and mouthpiece alone!
• The longer the wave, the greater the area of change needs to be to experience a result.
• This tool shows the fundamental tones, or "open" notes. That is, notes made by not manipulating the length of the instrument with valves or slides. For example, to see the tone positions for "1st position" or "2nd valve", add the length of the 2nd slide (or in the case of the trombone, the additional length that 1st position adds) to the overall length of the instrument. For additional valve combinations or lide positions, follow the same procedure. Do not forget to adjust the instrument key when doing so to avoid confusion.
• "Length" = Instrument length from the mouthpiece rim to the end of the bell, with instrument tuned.
• When possible, adjust the middle of the instrument to minimise affecting multiple notes. Leave the bell and mouthpiece alone!
• The longer the wave, the greater the area of change needs to be to experience a result.
• This tool shows the fundamental tones, or "open" notes. That is, notes made by not manipulating the length of the instrument with valves or slides. For example, to see the tone positions for "1st position" or "2nd valve", add the length of the 2nd slide (or in the case of the trombone, the additional length that 1st position adds) to the overall length of the instrument. For additional valve combinations or lide positions, follow the same procedure. Do not forget to adjust the instrument key when doing so to avoid confusion.
"...Schilke and Boosey and Hawkes (Smith, R.A. & Daniell, G.J., Nature 262, p. 761-765, 1976.) have developed techniques where the intonation of a trumpet can be improved. Both are based on the original work attributed to Mahillon (Belgium) and Blaikley (England) towards the end of the 19th century, who found that small changes in the bore cross section near a pressure node (zero) or antinode (maximum) of the standing wave would change the resonance frequency. (A decrease in area at a pressure antinode produces an increase in that frequency and an increase in area gives a frequency decrease. At a pressure node the effects of changing the area are reversed.)..." http://la.trompette.free.fr/Smith/ITG78en.htm






References:
 Die Stimmungsbeeinflussung von Metallblasinstrumenten nach Walter Krüger
Die Stimmungsbeeinflussung von Metallblasinstrumenten nach Walter Krüger
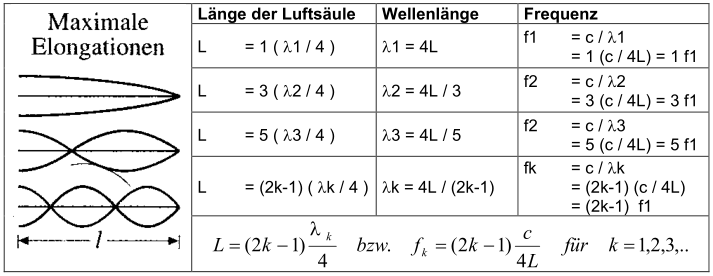
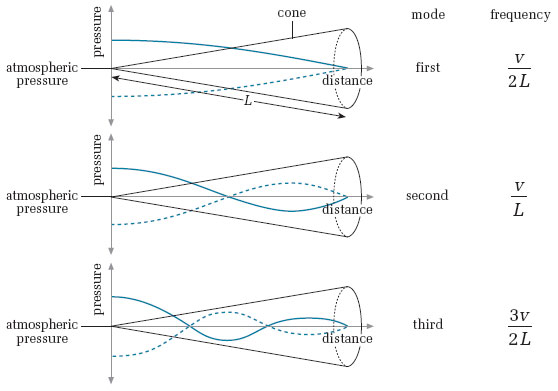
 5.11 Vibrating air column: standing waves in a conical tube
5.11 Vibrating air column: standing waves in a conical tube
 The fundamental mathematical and acoustical properties of woodwind and brass instruments - Krush, Joseph Martin 1978
The fundamental mathematical and acoustical properties of woodwind and brass instruments - Krush, Joseph Martin 1978
 Schwingungslehre in Kursstufe - Ernst Schreier
Schwingungslehre in Kursstufe - Ernst Schreier
 The Physics of Inner Brass and the Acoustical Effects of
Various Materials and Their Treatment - Renold O. Schilke
The Physics of Inner Brass and the Acoustical Effects of
Various Materials and Their Treatment - Renold O. Schilke
 Theorie, "The conical bore in musical acoustics"
Theorie, "The conical bore in musical acoustics"
http://la.trompette.free.fr/Smith/ITG78en.htm
http://la.trompette.free.fr/Smith/Nature/intonation.htm
http://newt.phys.unsw.edu.au/jw/brassacoustics.html#pipe